Databases are crucial for storing and managing data efficiently. There are several types of databases, each with its own strengths and use cases. Let's explore some of the most common types:
1. Relational Databases
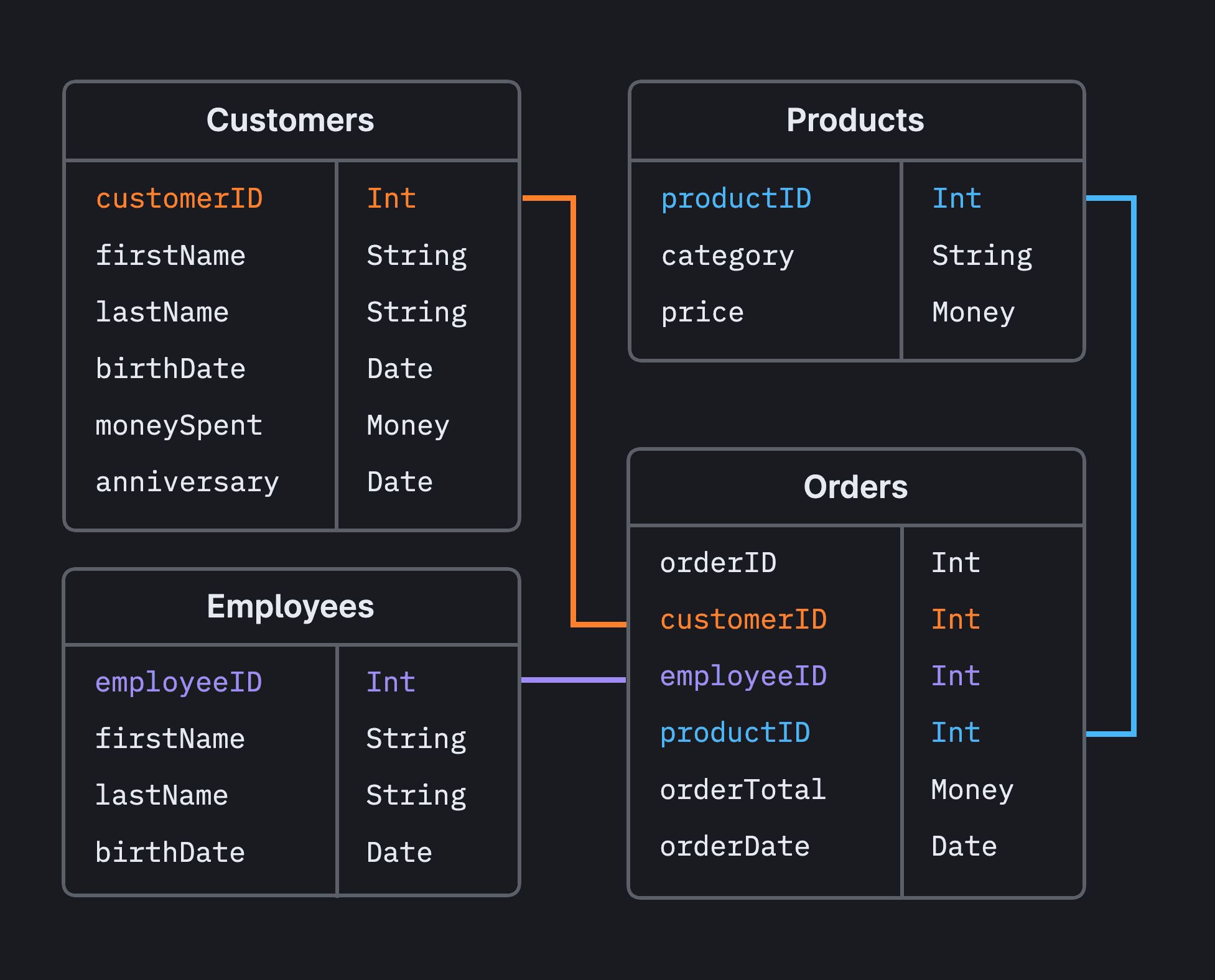
Relational databases organize data into tables with rows and columns, and they use structured query language (SQL) for querying and managing data. They ensure data integrity through relationships and support transactions. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle Database.
2. NoSQL Databases
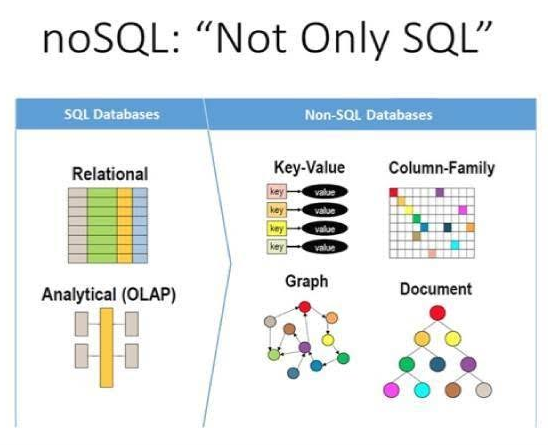
NoSQL databases, or "Not Only SQL" databases, are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. They provide flexible schemas, horizontal scalability, and high performance for distributed data storage and processing. Examples include MongoDB, Cassandra, and Redis.
3. NewSQL Databases

NewSQL databases combine the benefits of traditional relational databases with the scalability and performance of NoSQL databases. They aim to provide ACID compliance, strong consistency, and horizontal scalability for modern applications with high transactional loads. Examples include Google Spanner, CockroachDB, and VoltDB.
Choosing the Right Database
The choice of database depends on factors such as data structure, scalability requirements, consistency needs, and performance goals. Understanding the characteristics and use cases of different types of databases helps in selecting the most suitable option for a particular application.
Conclusion
Databases are foundational components of modern software applications, and choosing the right type of database is essential for building scalable and efficient systems. Whether it's relational, NoSQL, or NewSQL, each type of database offers unique features and benefits to address diverse data management challenges.
